Keeping the balance of the container is of great significance especially when loading heavy cargoes. Because the offset of the center of gravity may lead to cargo damage during the shipping process, which will result in unnecessary shipping costs.
For example: if the offset of the center of gravity is not within a reasonable range while lifting the container on and off at the terminal, there is a risk of the container falling, causing serious cargo damage and other economic losses.
In general, transportation authorities have strict constraints on the offset of the center of gravity. If the offset is not within the constrained range, there will be penalties such as adjustment fees, high fines, or being required to be pulled back to reload, which will not only cause huge economic losses but also delays in delivery and inability to deliver goods on time, in the end resulting in reduced customer satisfaction, customer complaints and even loss of customers.

The reason why the offset of the center of gravity may cause these tricky problems for companies is because purely depending on the manual loading experience isn’t scientific enough to predict the potential offset degree, therefore may causing immeasurable losses to the enterprise.
For example, a motorcycle parts company in Chongqing , China has a lot of orders of cargoes that need to be transported through railway. It often happens that the center of gravity offset does not meet the requirements of the Chongqing Railway Bureau, resulting in high fines, and the inability to deliver goods to customers on time because of reloading. This has brought them a lot of trouble. It wasn’t until they used LoadMaster load planning software that the problem was solved.

So, how does LoadMaster load planning software help various companies deal with the offset of the center of gravity? Let’s take a look!
When calculating the load plan, LoadMaster also provides a balance analysis of the center of gravity offset enabling users clearly see the the offset degree and allowing the offset of the center of gravity predictable and controllable.
Center of gravity balance analysis for railway authorities: By checking the “front and rear weight offset” and “left and right weight offset”, fines can be avoided as long as the goods are within the required range of offset.
Center of gravity balance analysis for ocean shipping: Users can know about the offset degree by checking the “Length Direction Core Offset” and “Width Direction Core Offset”. According to experiments conducted by Japanese experts, when the container is fully loaded, the safety of the cargo can be ensured if the front, rear, left, and right offsets are within 10%.
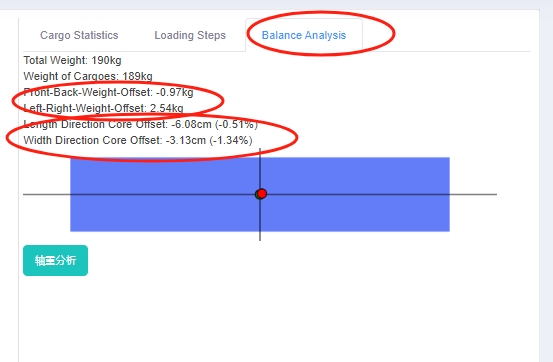
If the effect of the load plan automatically generated by the software cannot meet the requirements of the range of the center of gravity offset, you can use manual edit to adjust the placement of the cargo. On the right corner of the manual edit interface, real-time balance analysis is displayed to help check if the offset is within the required range.
 This picture shows a container loading site.
This picture shows a container loading site.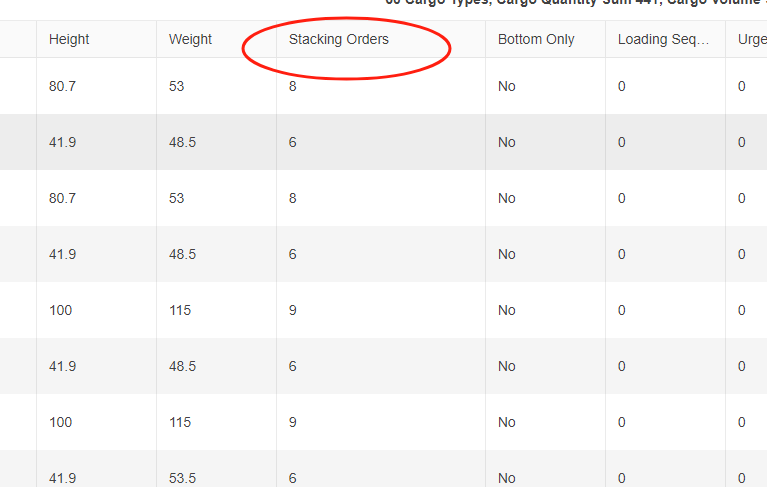



 This picture shows an arrow with downward trend.
This picture shows an arrow with downward trend. This picture shows a truck driving on the road.
This picture shows a truck driving on the road.
 This picture shows a container fully loaded with cargoes.
This picture shows a container fully loaded with cargoes. The picture shows different kinds of furniture.
The picture shows different kinds of furniture. The “Stand” “Stand&Rotate” in the template.
The “Stand” “Stand&Rotate” in the template. The “Side” “Side&Rotate” in the template.
The “Side” “Side&Rotate” in the template.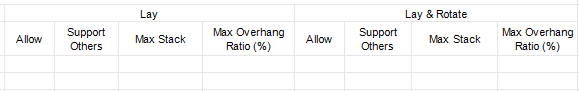 The “Lay” “Lay&Rotate” in the template.
The “Lay” “Lay&Rotate” in the template.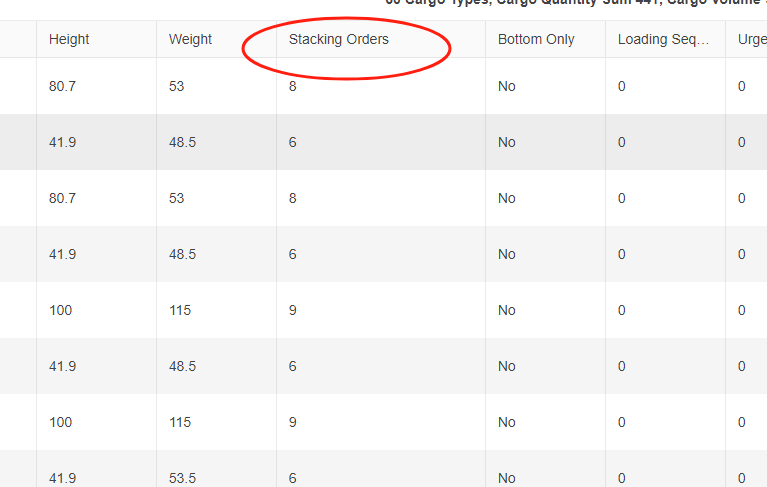 Stacking Orders column in the software.
Stacking Orders column in the software.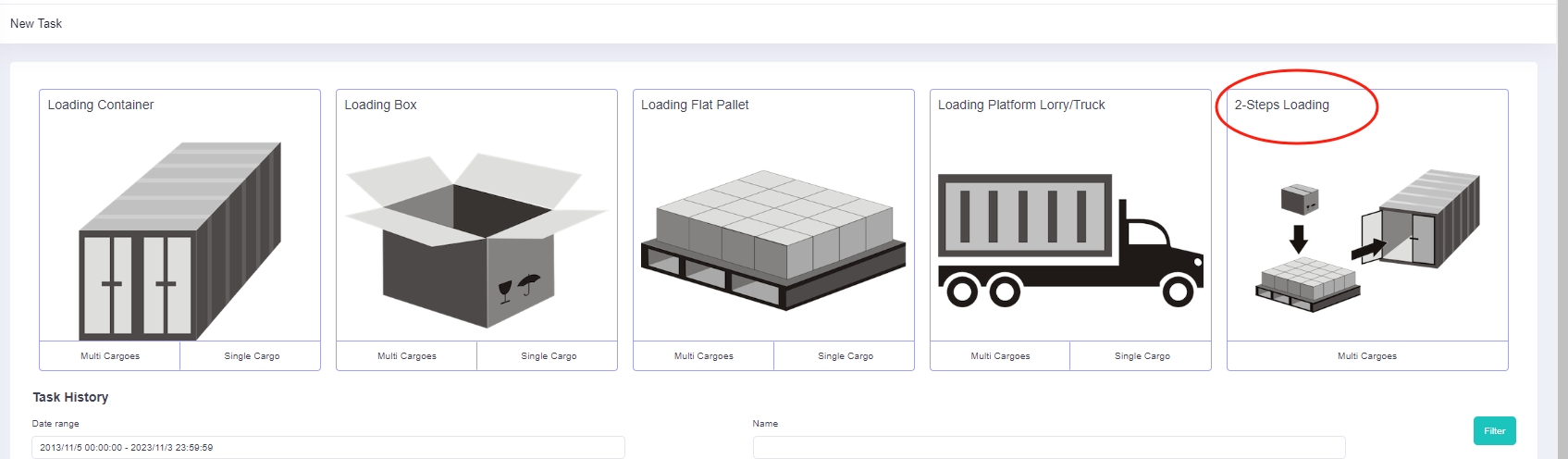 Two-steps loading task.
Two-steps loading task.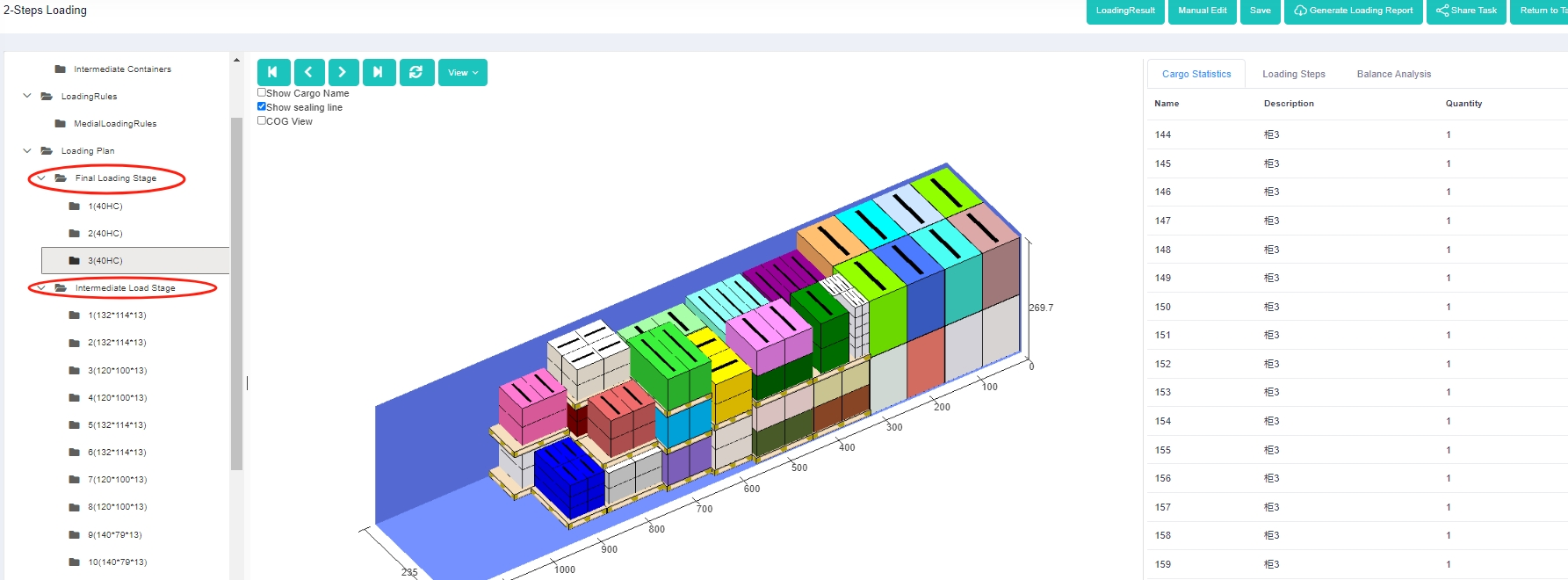 3d load plan of a two-steps loading task.
3d load plan of a two-steps loading task.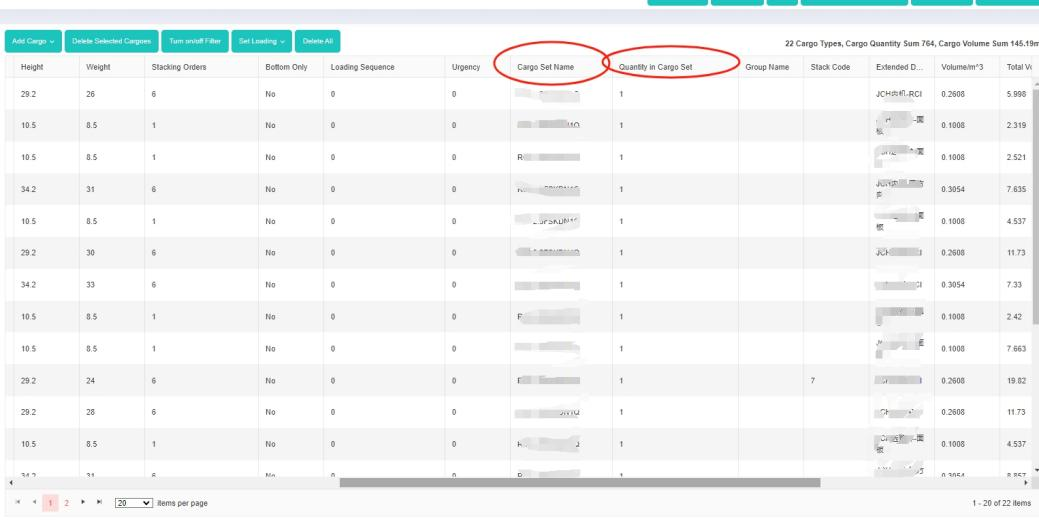 “Cargo set name” and “Quantity in cargo set” columns in the software.
“Cargo set name” and “Quantity in cargo set” columns in the software.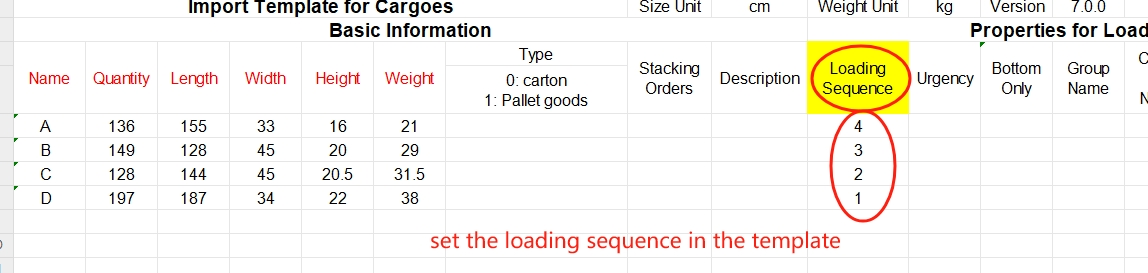 Set the loading sequence in the template.
Set the loading sequence in the template.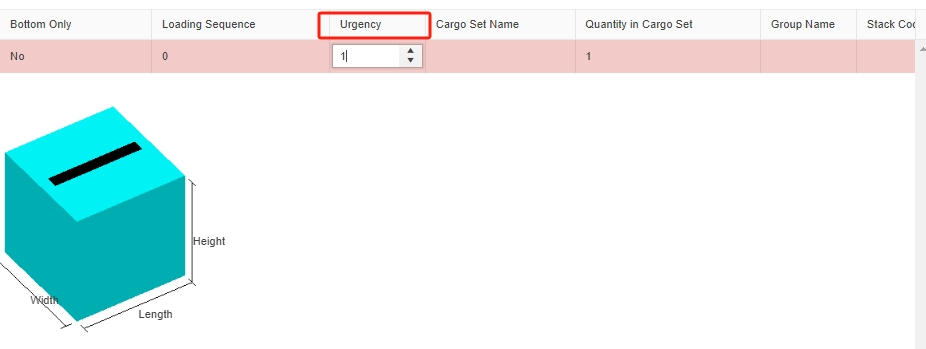 Set the Urgency in the software.
Set the Urgency in the software.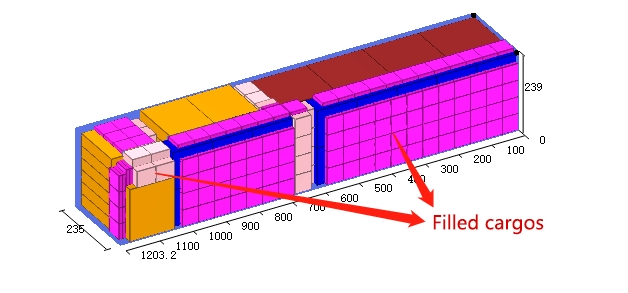 3d load plan that shows filled cargoes filling in the remaining room in a container.
3d load plan that shows filled cargoes filling in the remaining room in a container. This is a picture that shows increasing money.
This is a picture that shows increasing money. The picture of different kinds of home appliances.
The picture of different kinds of home appliances. This is a picture of a pallet loaded with cargo.
This is a picture of a pallet loaded with cargo. A thumbs-up gesture.
A thumbs-up gesture. A forklift is lifting cargo to load them into the container.
A forklift is lifting cargo to load them into the container. Some people are loading cargo on site.
Some people are loading cargo on site. This is a picture of a ship tilting over the sea.
This is a picture of a ship tilting over the sea.

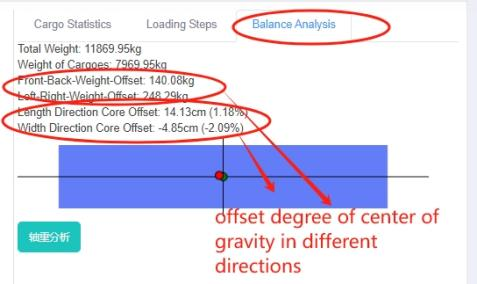 Balance analysis details.
Balance analysis details.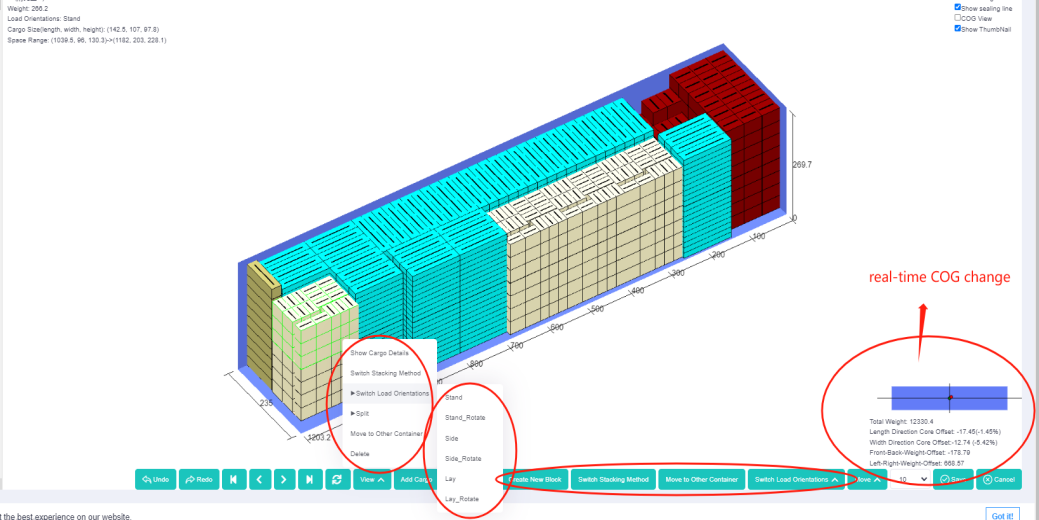 Manual edit interface, with real time COG change.
Manual edit interface, with real time COG change.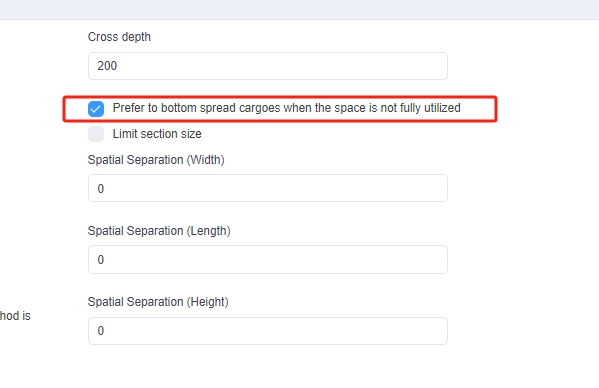 Loading rule “Prefer to bottom spread cargoes”.
Loading rule “Prefer to bottom spread cargoes”.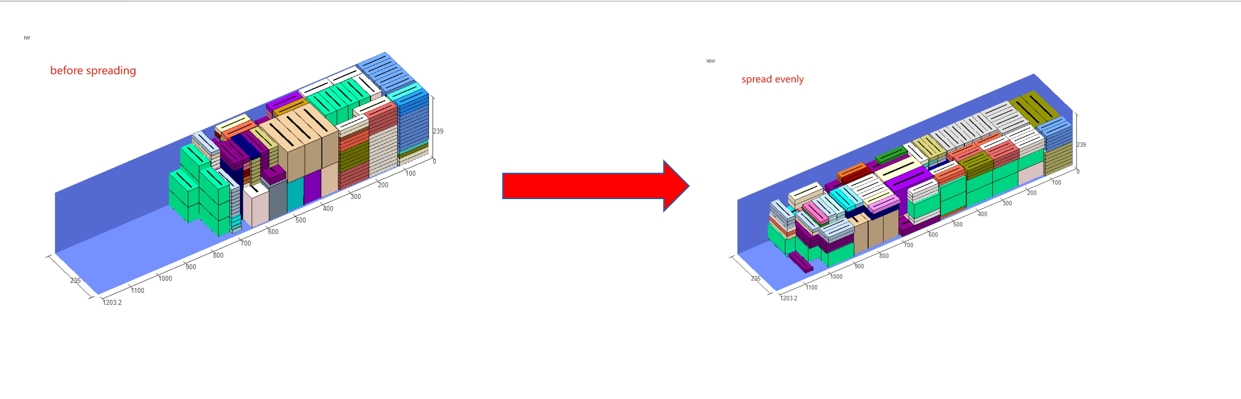 Comparison between “not spreading” and “spreading bottom”.
Comparison between “not spreading” and “spreading bottom”.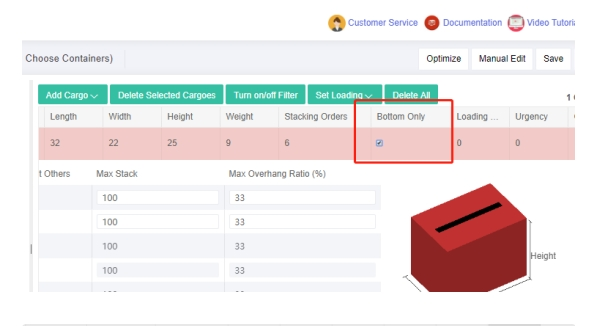 Bottom only column in the software.
Bottom only column in the software.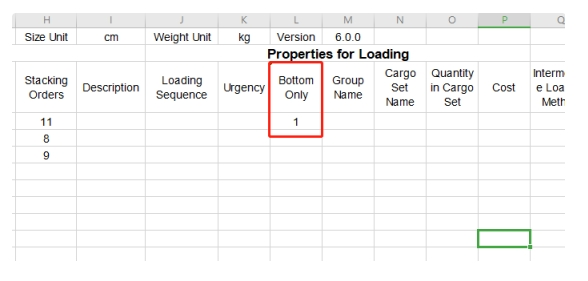 Bottom only column in the template.
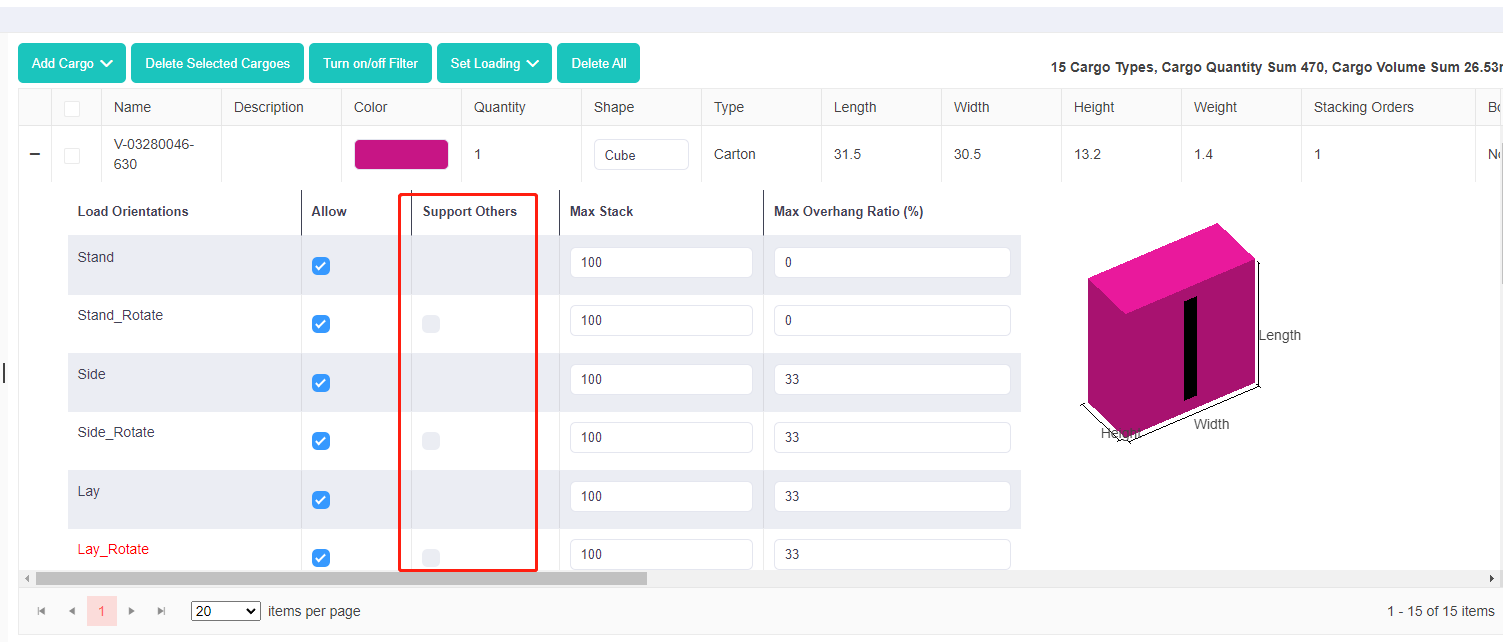
Bottom only column in the template.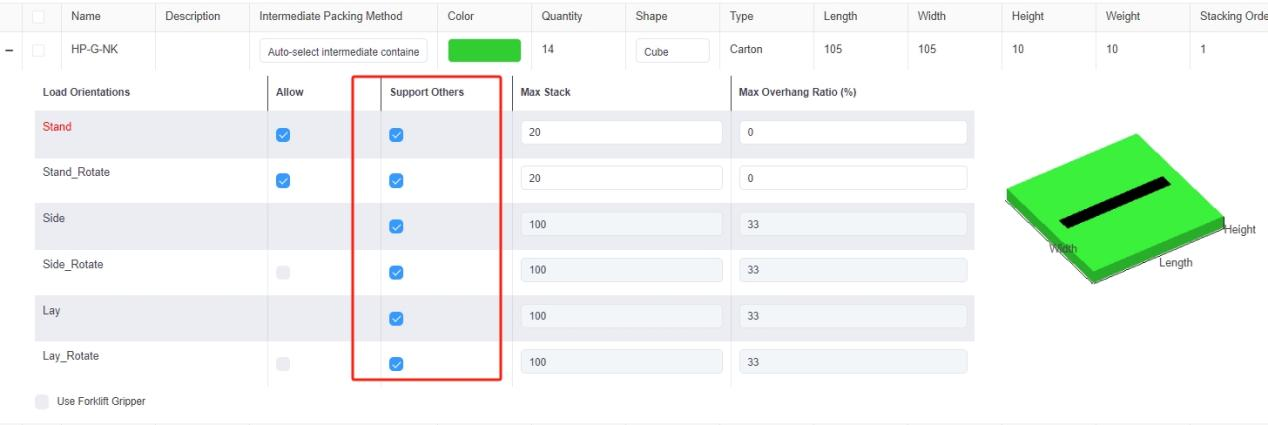 Support Others column in the software.
Support Others column in the software. Support Others column in the template.
Support Others column in the template.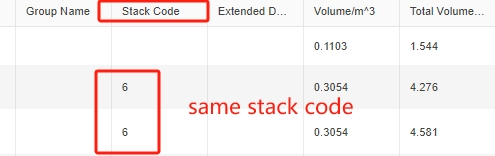 Same stack code.
Same stack code.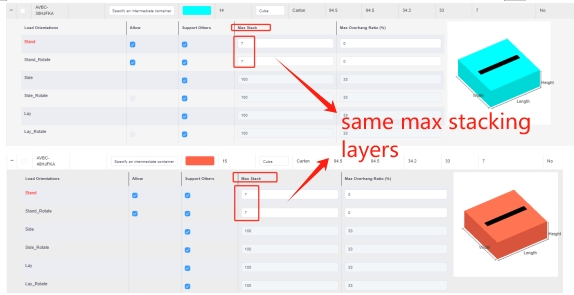 Same Max Stack.
Same Max Stack.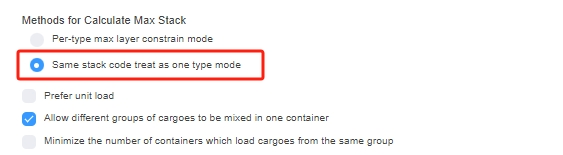 Loading rule “Same stack code treat as one type mode”.
Loading rule “Same stack code treat as one type mode”. Loading rule “Only allow items with the same or similar length and width to stack together”.
Loading rule “Only allow items with the same or similar length and width to stack together”.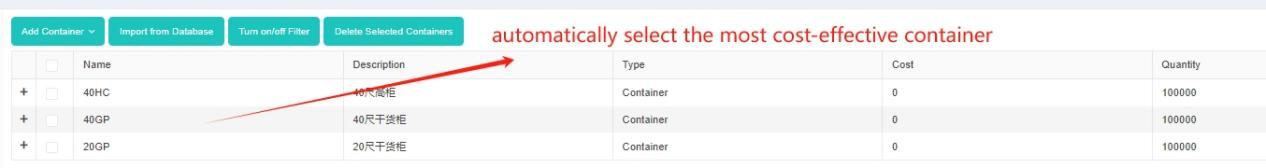 Interface of adding containers.
Interface of adding containers.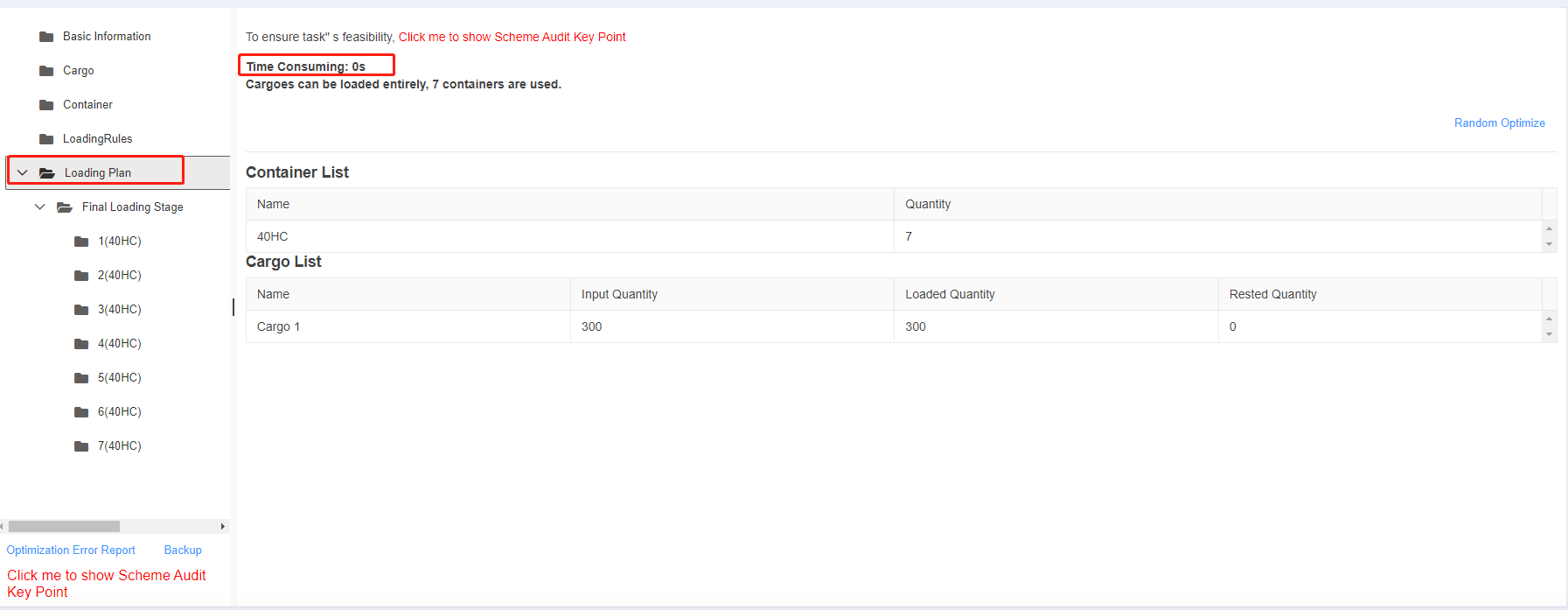 The load plan is calculated very fastly.
The load plan is calculated very fastly.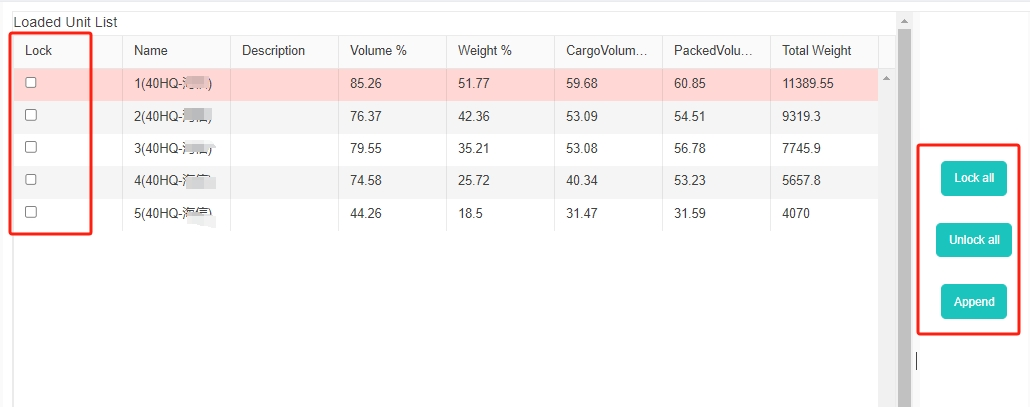 The interface of loacking some containers and only adjusting the rest.
The interface of loacking some containers and only adjusting the rest.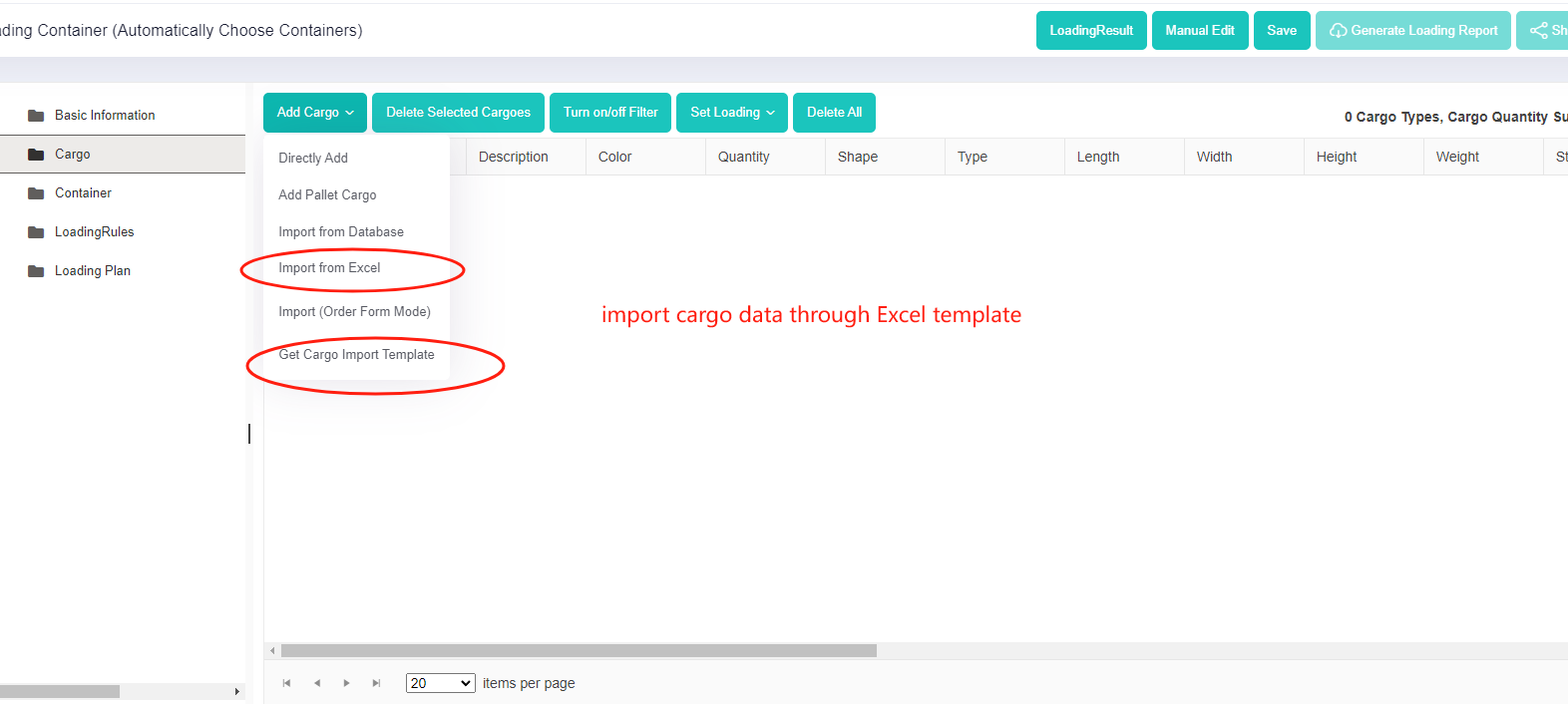 Import cargo data through Excel template.
Import cargo data through Excel template.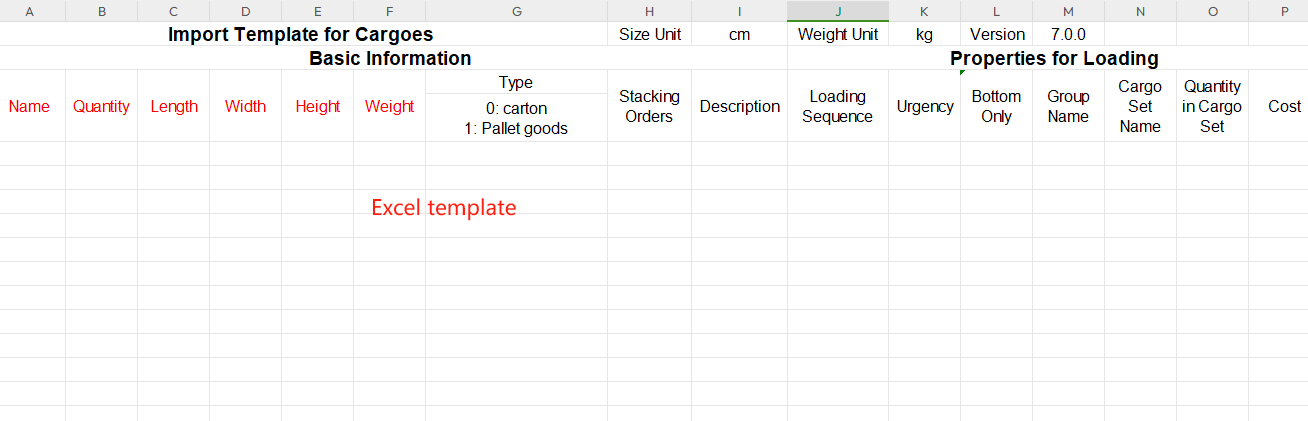 Excel import template for cargoes.
Excel import template for cargoes.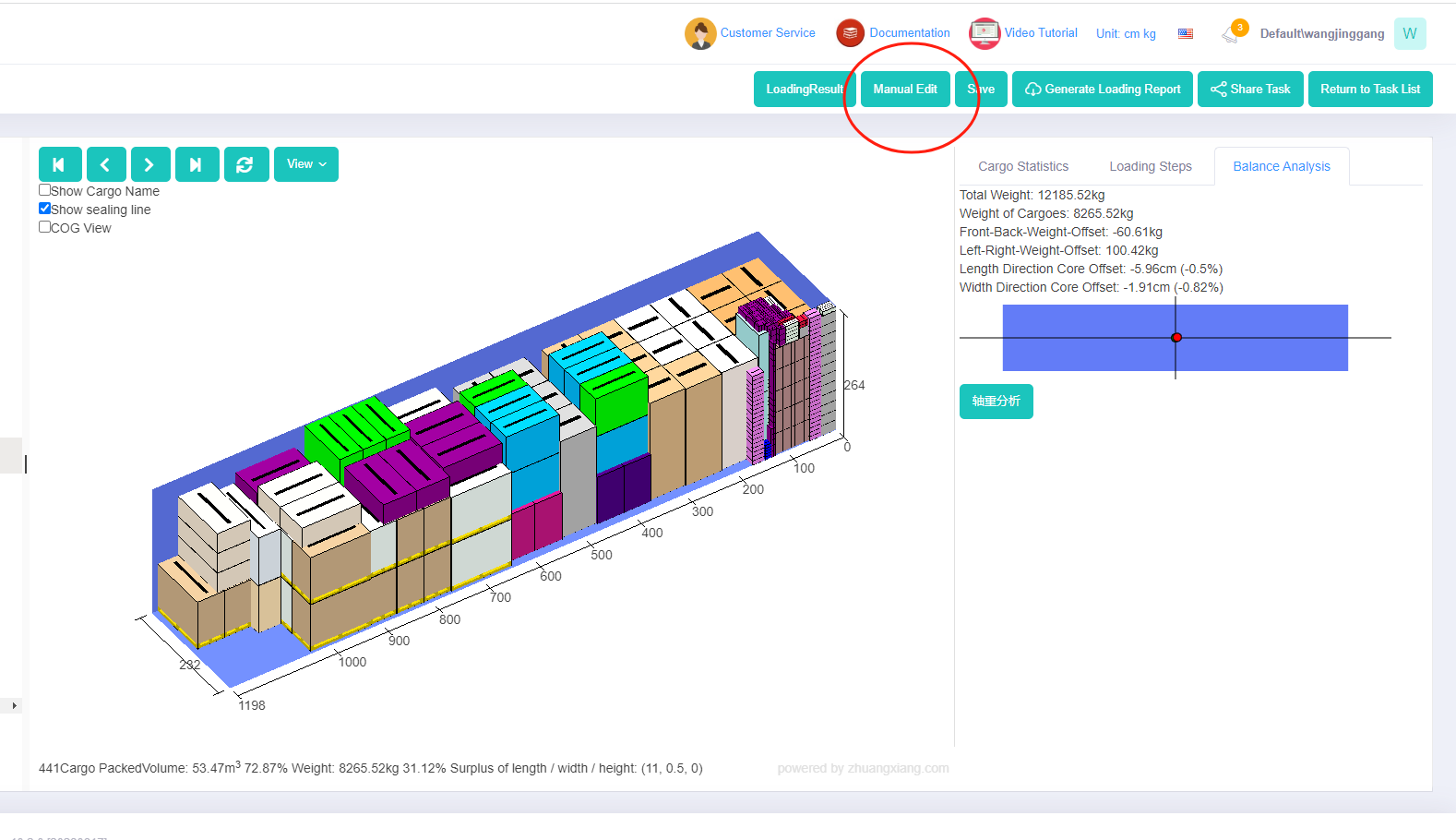 Manual edit button.
Manual edit button.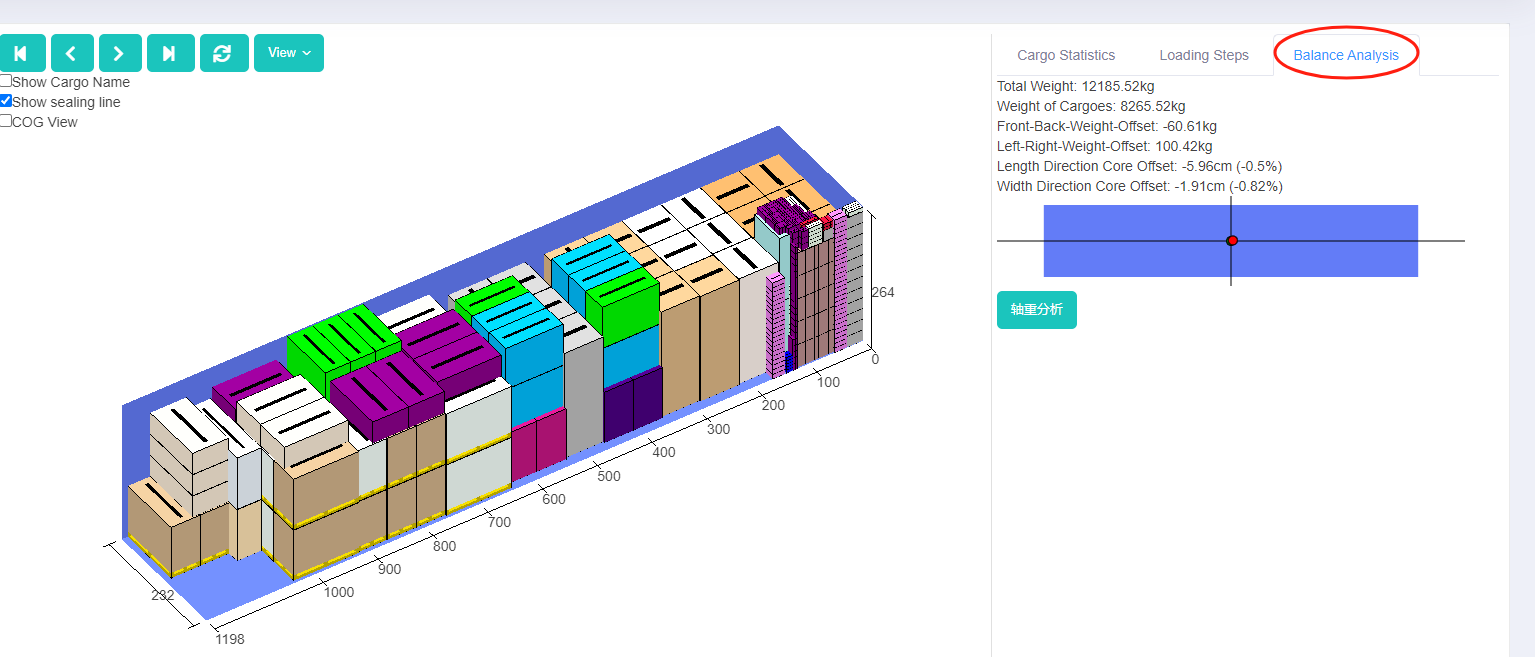 Balance analysis on 3d load plan.
Balance analysis on 3d load plan. The picture shows kinds of auto parts.
The picture shows kinds of auto parts. The picture of palletized cargo.
The picture of palletized cargo. Palletized cargo waiting to be loaded into the container.
Palletized cargo waiting to be loaded into the container.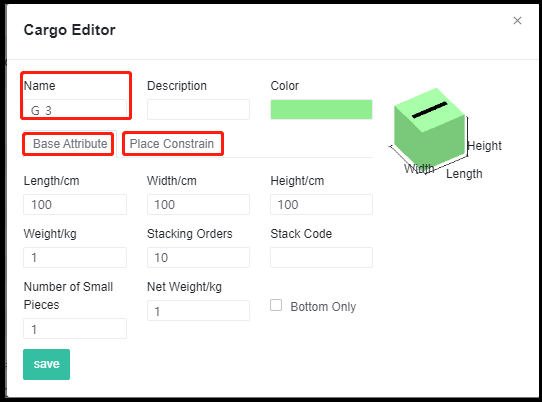 The editing interface of adding cargo to the database.
The editing interface of adding cargo to the database.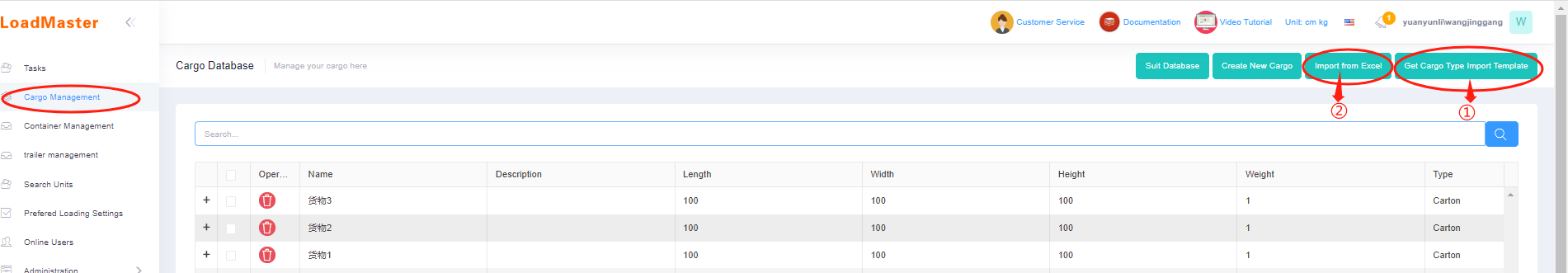 Add cargo to the database through excel.
Add cargo to the database through excel.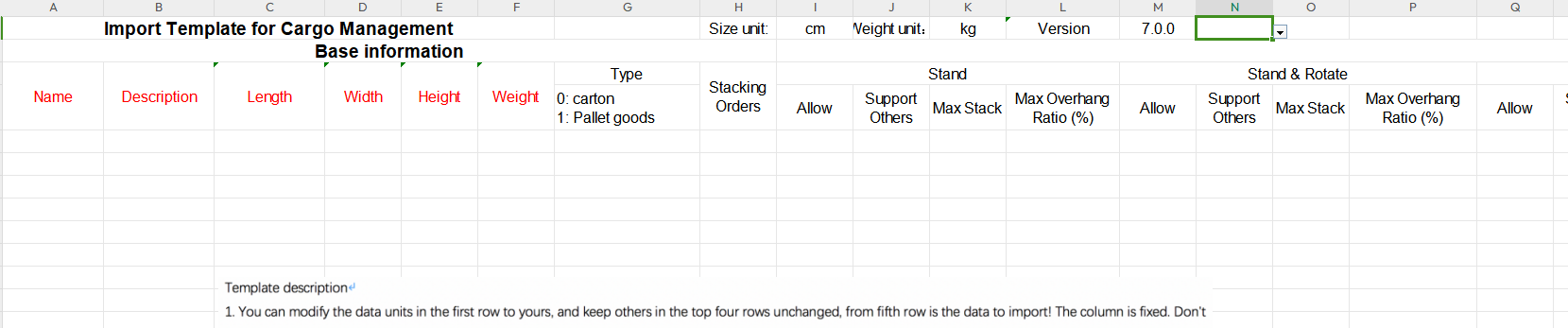 The import template for cargo management.
The import template for cargo management.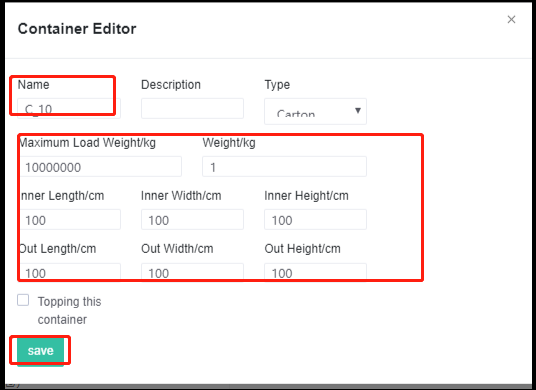 The editing interface of adding container to the database.
The editing interface of adding container to the database.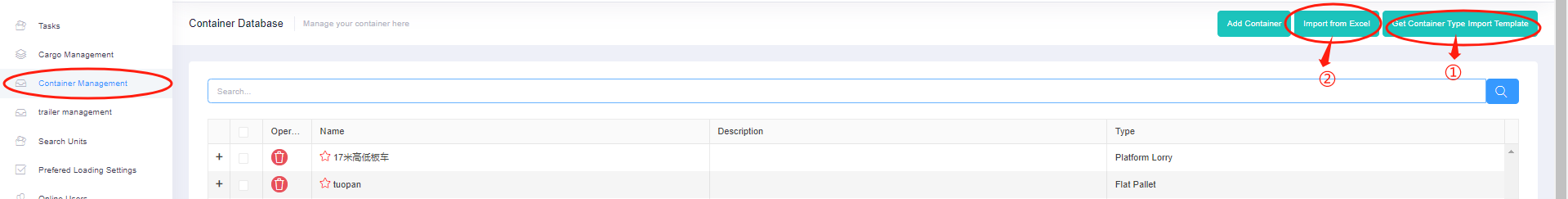 Add container to the database through excel.
Add container to the database through excel.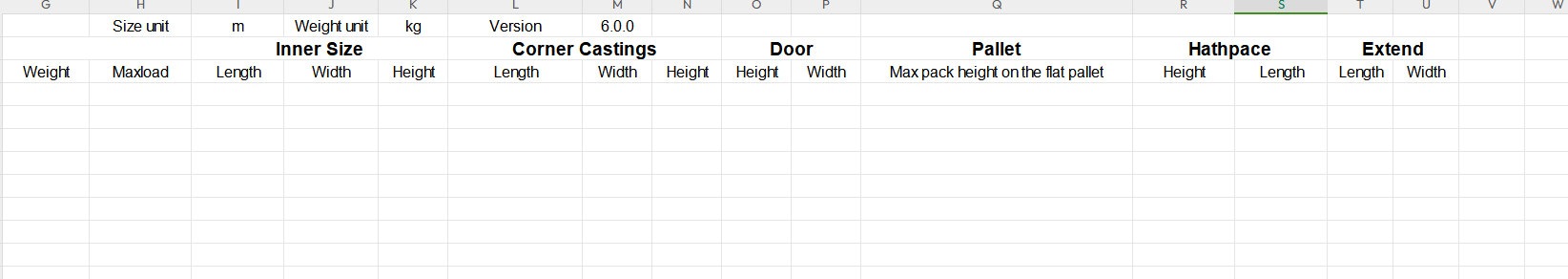 The import template for container management.
The import template for container management.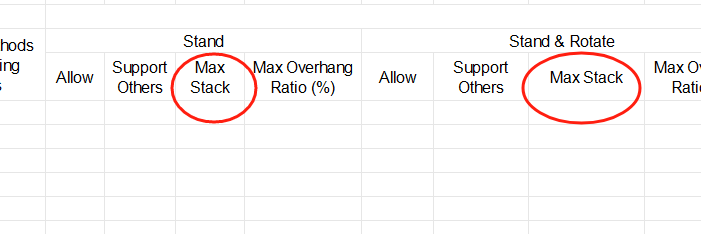 Max Stack in cargo import template.
Max Stack in cargo import template.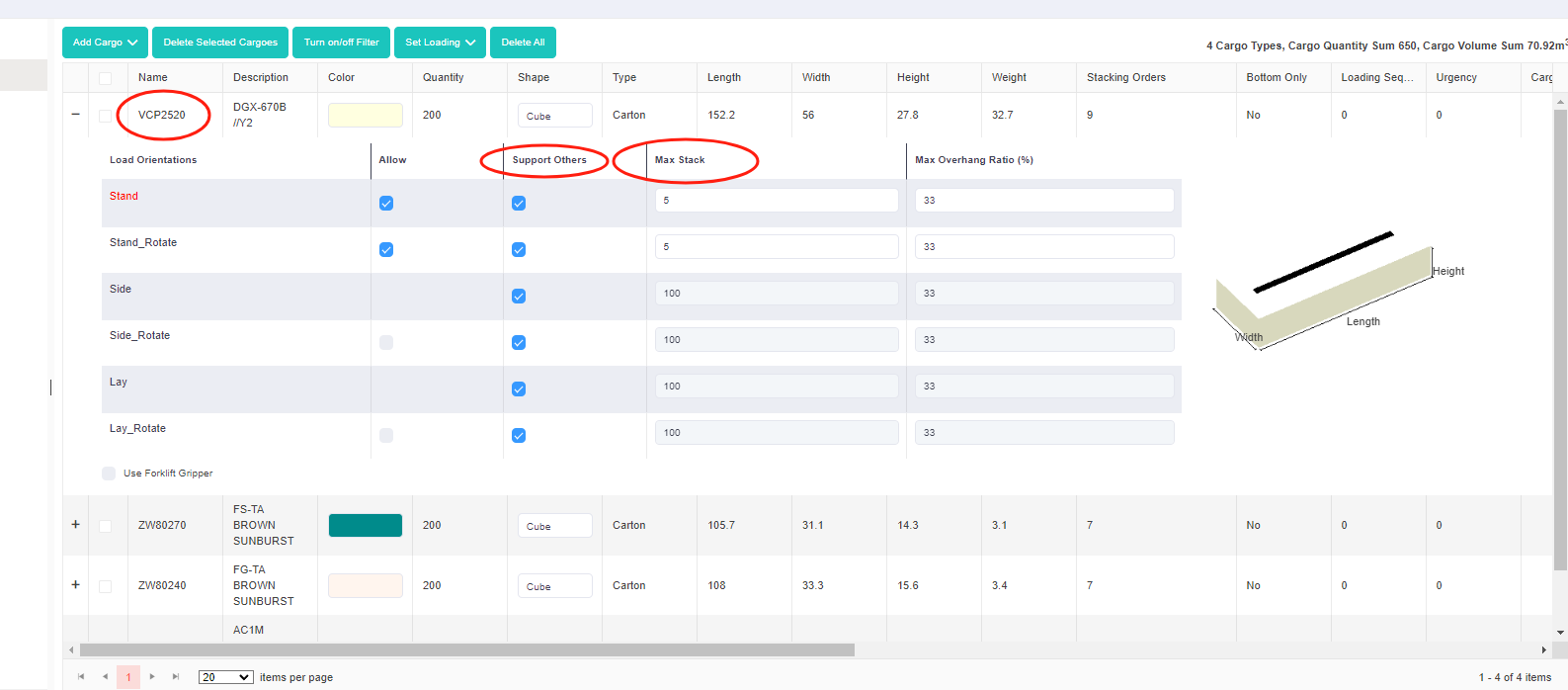 Support Others and Max Stack in the software.
Support Others and Max Stack in the software.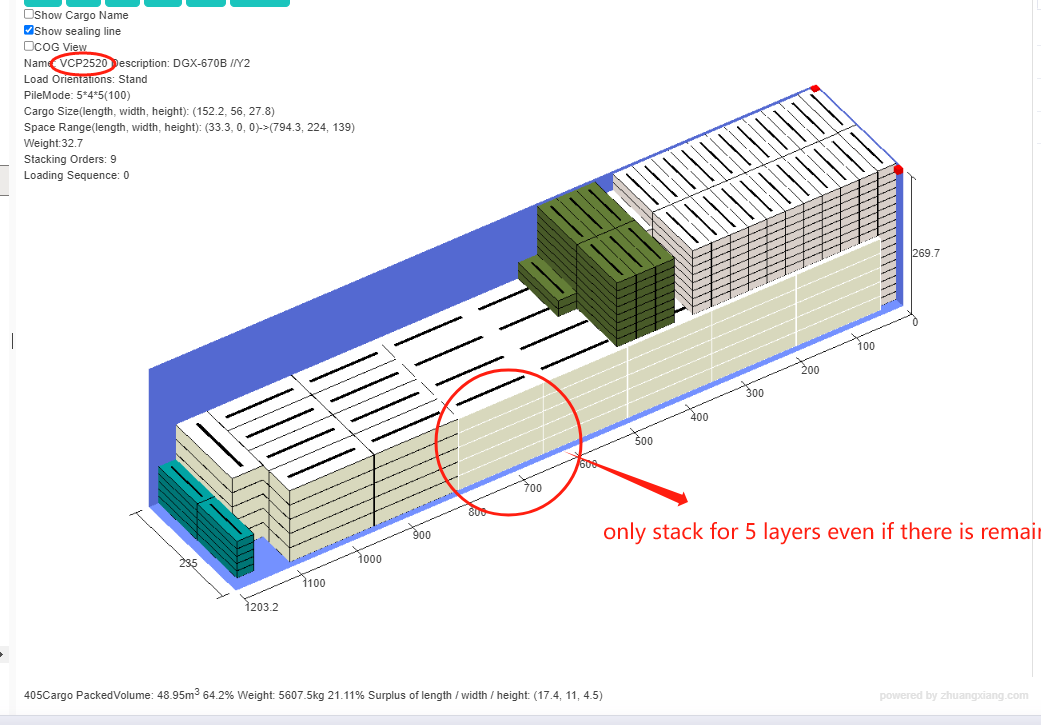 3d load plan that shows VCP2520 only stacks for 5 layers.
3d load plan that shows VCP2520 only stacks for 5 layers.